
Tools
and Technology
Topics Covered On This Page:
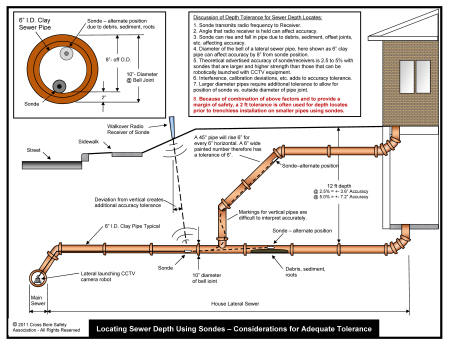
- Locating Sewers with Sondes - Considerations for Adequate Tolerance
- GIS Mapping of Sewers - One Cities Online System New Construction - Tools for Locating Crossings of Utilities
- Microphones as Acoustic Sewer Monitors for Cross Bore Identification - A summary of Questionaire
- Post Construction & Legacy Cross Bore Locating
- Emerging Tools & Technologies
- CCTV, GPS, GIS Project slide presentation, courtesy Cues, Inc.

New Construction - Tools for Locating Crossings of Utilities
- Visual
- Day-lighting by excavation
- Excavator - high risk, large foot print, high surface impact
- Digging by hand tools - medium risk, small footprint, medium surface impact
- Vacuum excavation - low risk, medium footprint, small surface impact
- Day-lighting by excavation
- Sondes, radio frequency transmitters and receivers
- Inserted into existing utility
- Lateral launched from main line robotic, surface controlled camera - low risk, no footprint, no surface impact, accuracy less than visual methods, pipes only, not always able to transverse offset joints or roots
- Push-rod camera - low risk, no footprint, no surface impact, accuracy less than visual methods, requires access to line by clean-out or interior of structure, pipes only, not always able to transverse offset joints or roots
- Inserted into existing utility
- Induced Electric - suitable only for metallic conductor utilities or utilities with locating wire, low risk, small foot print, minimal surface impact when connecting terminals need to be exposed, needs connecting points to surface, accuracy less than visual methods
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) - small foot print, no surface impact, not suitable for all soils, suitable for large areas or long runs, accuracy less than visual methods, needs in office interpretation
- Gyroscopes - low risk, no footprint, no surface impact, good accuracy reported, requires access to existing utilities for insertion, pipes only, not always able to transverse offset joints or roots, needs in office compilation.
Post Construction & Legacy Cross Bore Locating
- Observing loss of service
- Electric, communications, gas, water, etc.
- Observe escaping fluids or gases from pressurized utilities
- Note: Intersections of can be into both sewers and backfill of trenches, annular space around utility or pipe bedding allowing for unobserved transmission to structures and to other utility's or their backfill or annular space and connected structures.
- Visual
- Day-lighting by excavation
- Excavator - high risk, large foot print, high surface impact
- Digging by hand tools - medium risk, small footprint, medium surface impact
- Vacuum excavation - low risk, medium footprint, small surface impact
- Day-lighting by excavation
- Mainline CCTV with or without Sondes, inserted into existing utility
- Lateral launched from robotic, surface controlled main line camera - low risk, no footprint, no surface impact, accuracy less than visual methods, pipes only, not always able to transverse offset joints or roots
- Sonde receiver can be provided with GPS for recording of "X" and "Y" coordinates and vertical reading transmitted to truck/camera operator station
- Outputs provide work verification
- Outputs can be layered on to GIS mapping
- Can be accessed to reduce need for future locates
- Digitized of easy future access
- Can be integrated to internet accessible mapping for new construction locating needs
- Can be integrated to internet accessible for sewer service contractors to determine if an address has been determined to be cross bore free of gas lines in sewers
.
- CCTV, GPS, GIS Project slide presentation, courtesy Cues, Inc., PDF format, 2.9 MB
- Sonde receiver can be provided with GPS for recording of "X" and "Y" coordinates and vertical reading transmitted to truck/camera operator station
- Lateral launched from robotic, surface controlled main line camera - low risk, no footprint, no surface impact, accuracy less than visual methods, pipes only, not always able to transverse offset joints or roots
- Push-rod CCTV camera with or without Sondes, inserted into existing utility, low risk, no footprint, no surface impact, accuracy less than visual methods, requires access to line by clean-out or interior of structure, pipes only, not always able to transverse offset joints or roots
- Induced Electric - suitable only for metallic conductor utilities or utilities with locating wire, low risk, small foot print, minimal surface impact when connecting terminals need to be exposed, needs connecting points to surface, accuracy less than visual methods
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) - small foot print, no surface impact, not suitable for all soils, suitable for large areas or long runs, accuracy less than visual methods, needs in office interpretation
- Gyroscopes - low risk, no footprint, no surface impact, good accuracy reported, requires access to existing utilities for insertion, pipes only, not always able to transverse offset joints or roots, needs in office compilation.
Emerging Tools & Technologies
- Forward looking Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) tools
- Development by Trenchless Technology Center, Louisiana Tech University in association with others
- Accoustic
- Listening devices that help identify if a existing pipe is "hit" during new construction
- University of Birmingham (England), "Mapping the Underground" project
- Listening devices that help identify if a existing pipe is "hit" during new construction
- Home
- History
- News
-
Leading
Practices
-
Legacy Cross
Bores
-
New
Construction
-
System
Integrity
-
Risk Evaluation
-
Drain
Cleaner Safety
-
Videos/Websites
-
Photos-Cross Bores+
-
State Locating Reguirements
-
Papers
and Presentations
-
Tools and Technology
-
Information
Sources
-
Join Now -
Membership
-
Contact
Us
-
Events
-
Directors
-
Search